A tension pneumoperitoneum occurs when air becomes trapped within the peritoneal cavity. This occurs because the peritoneal cavity is unable to continue to expand as more air leaks into it. This trapped air eventually causes respiratory depression and hypoxia because the patient’s diaphragm is unable to move inferiorly to allow adequate filling of the lungs with oxygen. The trapped air also causes the patient’s blood pressure to drop because it does not allow blood to return to the heart.
A tension pneumoperitoneum is a life-threatening emergency. Similarly, a pneumothorax occurs when air becomes trapped in the chest cavity producing a collapse of the lung(s). A pneumothorax causes hypoxia because the lungs cannot expand properly. This is especially dangerous in patients with underlying COPD due to preexisting pulmonary compromise.
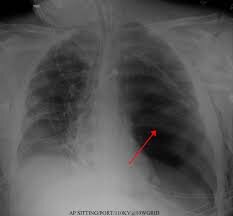
A tension pneumothorax occurs when the pressure builds up within the lung cavity to the extent that it does not allow expansion of the lung and thus places pressure on the heart, larger blood vessels and even the unaffected lung and, again, is a life-threatening emergency.
Tension pneumothorax medical expert witness specialties include critical care medicine, emergency medicine, EMT, trauma, cardiothoracic surgery, anesthesiology, cardiac anesthesiology, and obstetric anesthesiology.
IF YOU NEED A Tension Pneumothorax MEDICAL EXPERT, CALL MEDILEX AT (212) 234-1999.
Image courtesy of James Heilman, MD. A tension pneumothorax. This file is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-Share Alike 3.0 Unported license.